ECN site code: R27
DEIMS.iD: https://deims.org/8747ccf7-52af-4a83-a558-71a768b81a30
ECN monitoring by: The James Hutton Institute
Co-located terrestrial site: Glensaugh (T02)
The ECN freshwater sampling site, Birnie Burn is co-located with the James Hutton Institute's terrestrial site at Glensaugh. Glensaugh Research station is located 35 miles south west of Aberdeen, NE Scotland on the edge of the Grampian hills and covers over 1100 hectares. There is a small amount of woodland (5ha) and some short term and permanent grassland (150ha) but the dominant cover is semi-natural vegetation which accounts for the remaining area.
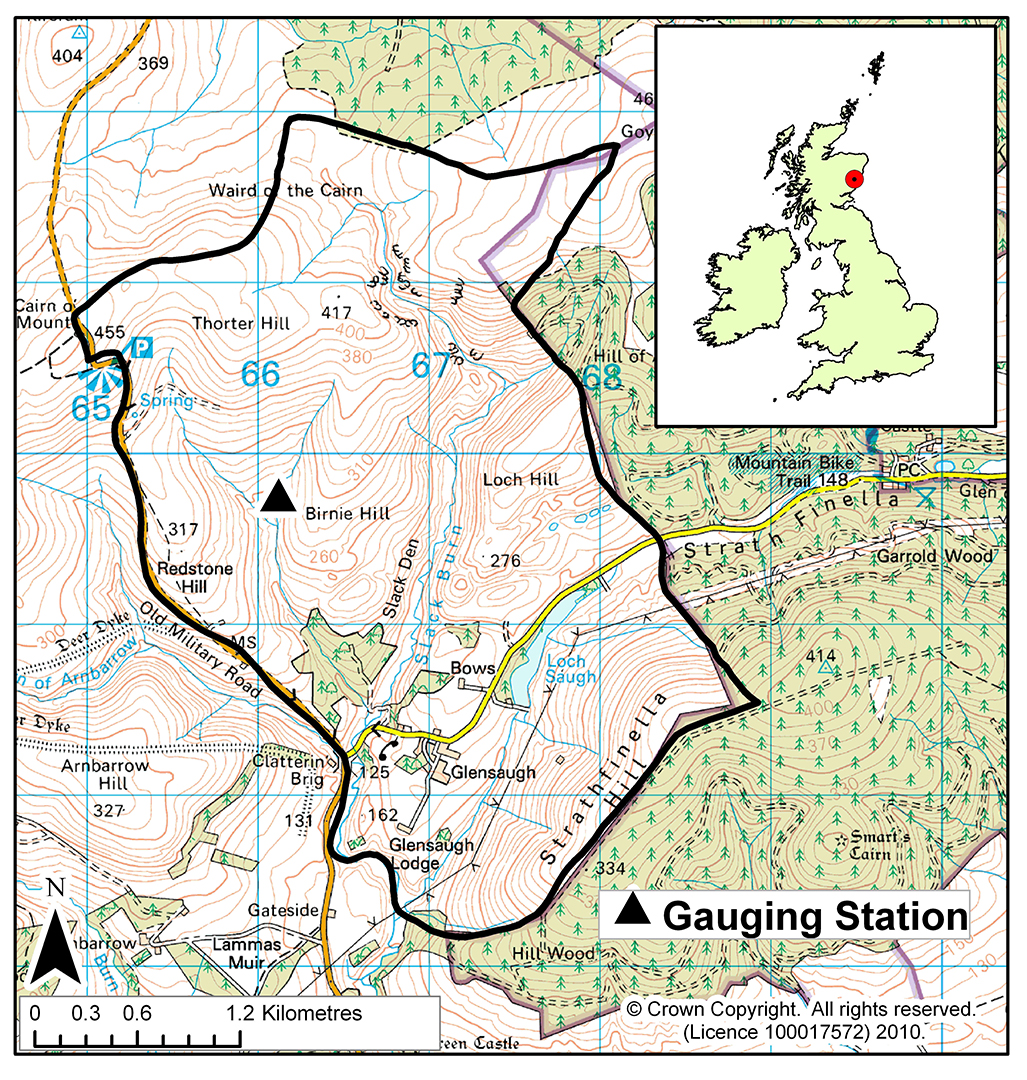
The Birnie Burn drains a small upland catchment of 0.8 km2 located toward the northern boundary of the research station. The highest hills in the catchment are to the North where they reach an altitude of around 450m. The ECN sampling point and gauging station are located less than 1km south of the stream source at an altitude of 240m a.s.l. The soils and the vegetation within the catchment area can be broadly classified into three zones. The upper zone (>400m a.s.l.) is characterised by hill peats developed on gentle slopes and covered by peat mosses (Sphagnum sp) and cotton grass (Eriophurum vaginatum). The middle zone (350-400m a.s.l.) features freely drained podzols that have developed in thin glacial till on the steeper slopes. The dominant vegetation types in this zone are heather (Calluna vulgaris), blaeberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) and wavy hair grass (Deschampsia flexuasa). The lower zone (220-350m a.s.l.) has freely draining iron podzols developed on thin glacial tills on steep heather and blaeberry covered slopes.